Are you looking to make a WordPress website? WordPress is the most popular content management system (CMS) that allows you to create and manage websites easily.
Whether you’re a blogger, freelancer, or business owner, WordPress offers a minimal learning curve, multiple ways to customize it, and create any website your heart desires.
In this post, we’ll show you how to make a WordPress website, including purchasing a domain name and hosting to designing and launching your website.
This tutorial guide is useful for all users of all ages and skill levels. If you want to do it by yourself, then please continue to read this post, our beginner-friendly guide on how to make WordPress websites.
Also Read: A WordPress Plugin: The Complete Guides 2023
Here is an ultimate overview from start to finish of all the steps we’ll walk you through in this guide.
- Why choose WordPress
- Find and register a domain name
- Choose the best web hosting
- Install WordPress
- Installing a template and customizing your site’s design
- Creating pages in WordPress
- Customizing WordPress with addons and extensions
- Resources to learn WordPress and get support
- Taking it further, building websites with more features (eCommerce stores, blogs, membership sites, selling online courses, and more).
Before we start creating a website, let’s cover some of the most commonly frequently asked questions.
First, no you DO NOT need to be a web developer to create a custom website. Our guide is written for non-techy users, and we will show you a no-code solution to creating a WordPress website.
With that said, let’s look at all the things you need to build a website.
What do I need to build a WordPress website?
You’ll need the following three things to start your WordPress WordPress site.
- A domain name – this is the name of your website such as google.com
- WordPress hosting – this is where your website files are stored. <<<This is an affiliate link. If you purchase a paid plan I will receive a commission payment.>>>
How much does a WordPress website cost?
The answer to this question depends on what kind of website you are trying to build.
A typical personal website can cost as low as $99. The cost of a business website can range from anywhere between $100 per year to as high as $30,000 per year accordingly.
We recommend all our users start small and then add more features to your website as your business grows. This way you will save money and minimize potential losses while avoiding overspending.
In this guide, we’ll show you how to build a website for less than $99.
We will also show you how to take it further by adding more features to it in the future.
Which is the best website builder platform?
There are many website builders available that will help you set up a website. We recommend using self-hosted WordPress as your website platform.
WordPress is the most popular website platform in the world. It powers nearly 43% of all websites on the internet.
WordPress is free, open source, and comes with thousands of pre-built website designs and extensions. It is extremely flexible and works with almost every third-party tool and service available to website owners.
We use WordPress to build all our websites including, WPWebTools.
Step-by-step WordPress website design tutorial
This is a step-by-step tutorial on how to make a website. We have divided it into different steps, and we’ll walk you through everything from start to finish. Just follow the instructions, and you’ll have a professional-looking website in the end.
We will also point you in the right direction on how to take your website to the next level based on your needs.
Step 1. WordPress Website Setup
The most common mistake that beginners make is choosing the wrong website platform. Thankfully, you are here so you will not be making that mistake.
For most users, a self-hosted WordPress.org site is the perfect solution. It comes with thousands of designs and add-ons that allow you to create any kind of website you can think of.
WordPress is free for anyone to download and build any kind of website without any restrictions.
If WordPress is free, then the question is where is the cost coming from?
WordPress is free because you’ll have to arrange your own custom domain name and web hosting provider, which costs money.
A domain name is your website’s address on the internet. It serves as a human-readable label that allows users to navigate the internet easily. This is what your users will type in their browsers to reach your site (For example, wpwebtools.com or google.com).
Domain names can be registered with domain name registrars, which are organizations such as Hover, and Domain.com, etc that manage the allocation and maintenance of domain names on the internet. Users can register domain names for specific periods and renew them as needed.
Next, you’ll need website hosting. All websites on the internet need a web host to store their website files. This will be your website’s home on the internet.
Also Read: What is WordPress? A Complete guides 2023
A domain name typically costs $14.99/year and hosting costs start from $7.99/month. For those who prefer to use Hostinger, it typically costs $2.99 for hosting and a free domain name.
This is a lot for most people who are just starting the website.
Hostinger has agreed to offer our users a free domain name and over 77% off on web hosting and free domain names.
<<Click Here to Claim to The Exclusive Hostinger Offer>>This is an affiliate link. If you purchase a paid plan I will receive a commission payment.
Hostinger is one of the largest hosting companies in the world.
Note: At WPWebtools, we believe in transparency. If you purchase hosting using our referral link, then we will get a small commission at no additional cost to you. You will get a discount on hosting + free SSL + a free domain name.
Let’s go ahead and purchase a domain name and hosting.
First, you’ll need to go to the Hostinger Website in a new browser window and click on the ‘Claim deal’ button.
This button will bring you to a pricing page where you will need to choose a hosting plan for your website.
Premium and business plans are the most popular choices among our users.
You’ll need to click on Ad to Cart to choose the web hosting plan that you like and continue to the next step.
On the next screen, you’ll be asked to choose a period and create an account. All periods such as 12 months, 24 months, and 48 months have a free domain name for the first year except one month.
You should stick to a .com domain name. Domain names should be related to your business, easy to pronounce and spell, and easy to remember.
After choosing your domain name, click on the next button to continue.
Now you’ll be asked to provide your account information such as name, address, email, etc.
Next, you will add your payment information to finish the purchase.
After completing your purchase, you’ll receive an email with details on logging in to your web hosting control panel (hPanel).
This is your hosting account dashboard where you manage everything, like getting support, setting up emails, etc. Most importantly, this is where you’ll install WordPress.
Step 2. WordPress Website: Install WordPress
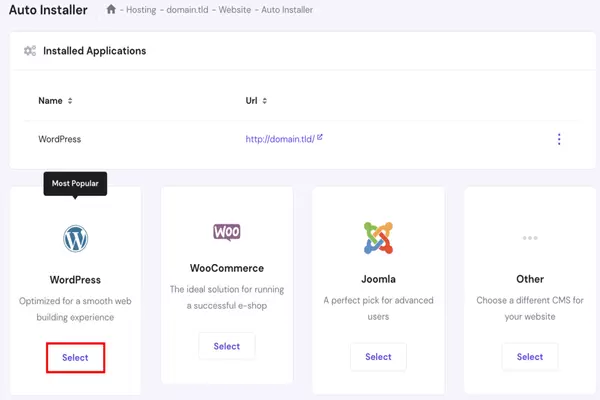
When you sign up with Hostinger, they will automatically install WordPress for you. They launched this one-click WordPress installer to make it easier for non-techy users to create their websites.
This means you need to log in to your Hostinger hPanel account and then click the Login to WordPress button to get started. This setup process has reduced the learning curve needed to make a website.
In this step, the following details are needed:
- URL ‒ your registered domain or address of your WordPress website.
- Language ‒ pick the primary language for WordPress.
- Username ‒ the username you’ll use to log into the WordPress dashboard.
- Password ‒ the password that you have to type in to enter the WordPress admin area.
- Email ‒ enter an active email address as it’ll be used for notifications and password reset.
- Website Title ‒ your website’s title
- Website Tagline ‒ a slogan or a short description of what your site is about.
You can also log in to the WordPress dashboard by going to yoursite.com/wp-admin/ directly from your browser.
Your Hostinger account can also be used to create multiple websites. Simply go to the My Sites section and use their one-click WordPress installer to make additional websites.
Once WordPress is set up, you’re ready to customize your website design by selecting a new template and creating new pages.
Now, let’s move on to the next step and choose a design for your website.
Step 3. Select Your Theme
A WordPress theme controls the visual appearance of your WordPress site.
WordPress themes are professionally designed templates you can install on your website to change its appearance.
You can browse through the WordPress theme gallery and pick one that matches your needs.
By default, each WordPress site comes with a basic theme.
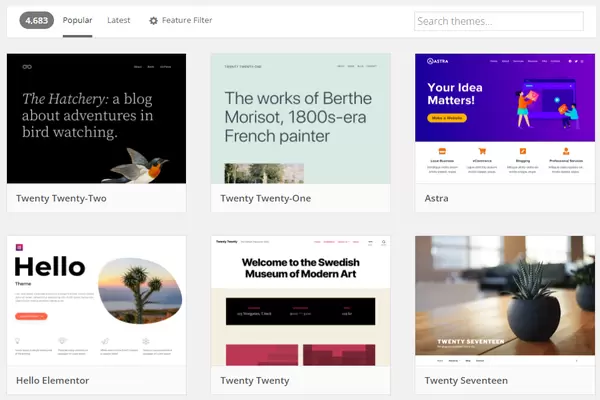
There are thousands of free and paid WordPress themes that you can install on your site.
You can change the WordPress theme for your website from the admin dashboard. Visit the Appearance » Themes page and click the ‘Add New’ button. Then select from the thousands of free themes available on the WordPress.org directory. You can sort them by popular, latest, featured, and other feature filters.
How to Install a Theme in WordPress from the WordPress.org directory
If you know the name of the free theme you want to install, you can look for it by entering it in the search field.
WordPress will show you the theme in search results. You will need to take your mouse over to the theme and then click on the Install button.
Once you have installed your theme, you can customize it by clicking on the Customize link under the Appearance menu.
This will launch the theme customizer, where you will be able to change your theme settings with a live preview of your website. You can customize a website color, blog, site identity, menus, widgets, and so on.
Step 4. Install Plugins to Customize Your WordPress Website
When you launch a WordPress site, you’ll have to choose and install plugins. WordPress provides tons of plugins that will help to extend the functionality of your sites such as admin enhancements, website security, and much more.
Some of the essential WordPress plugins that you can start with are:
- WooCommerce ‒ a useful plugin if you want to set up an online store. Perfect for website owners who wish to sell their products or services through their WordPress site. Note, if you’re planning to sell products online, it’s better to host your site with a platform that can guarantee seamless and secure transactions, for example, WooCommerce web hosting.
- Yoast SEO ‒ one of the best Search Engine Optimization (SEO) plugins. It helps you to publish higher-quality, search-optimized content.
- W3 Total Cache ‒ the plugin helps your site load faster on your readers’ computers on subsequent visits.
- Keyy Two Factor Authentication ‒ this plugin for security protects your website from unauthorized access. It lets you confirm your identity through a secondary device.
How to install plugins:
- Got to the Plugins section through your WordPress dashboard.
- Then click the Add New button at the top of the page.
- Type the keyword of the specific plugin that you need on the search field and press the Install Now button near the plugin. Or if you’ve downloaded the plugin in advance, simply click Upload Plugin. Then Choose File, select the plugin archive from the computer, and hit Install Now.
- To activate the plugin after the installation process, click the Activate Plugin.
Step 5. Add Content to Your WordPress Website
WordPress comes with two default content types posts and pages. Posts are part of the blogging functionality and appear in reverse chronological order (newer items are displayed first).
On the other hand, pages are meant to be static “one-off” type content such as your about page, contact page, privacy policy, home page, cookie policy page, etc.
By default, WordPress shows your blog posts on the front page of your website. You can change that, and make WordPress show any static page as the homepage of your website.
You can create a separate page for your blog or news section to show your recent posts. Alternatively, you can create a website without any blog section at all.
Let’s add some content to your website.
You’ll start by adding a few pages to your WordPress site. Don’t worry if you don’t have enough content for these pages. You can always edit and update them.
Head over to Pages » Add New page in the WordPress admin area. This will bring you to the page editor screen.
First, you need to provide a title for your page. Let’s call this page ‘Home.’
After that, you can add content in the text editor below. You can add text, links, images, embed videos, audio, etc.
After adding content to your page, you can click the publish button to make it live on your website.
You can repeat the process by adding more pages for different website sections. For example, an about page, contact us, and a blog page to display blog posts.
These pages are explained here:
- About – Your About page is where you get to tell the story of what your website is and why people should pay attention. This one page is a must-have for everyone who wants to learn how to make a website.
- Contact – this is where you can display some contact info along with a nice contact form, through which people can reach you directly (you can get such a form via the WPForms plugin. In WPWebTools, we use an awesome HTML Forms by ibericode).
- Privacy Policy – This page has become a hugely important element on today’s web.
- Portfolio – a place for you to showcase your past work.
- Store – a crucial thing if you want to sell anything from your e-commerce site. To make this work, you also need a popular WooCommerce plugin – the best e-commerce solution for WordPress.
- FAQs – if the scope of your new website requires some extra information for potential users.
Step 6: Consider starting a blog
A blog (as well as marketing through content – aka “content marketing” in general) is among the most effective ways to promote not only your website but also any products that you might want to sell through that website.
And it’s not just me saying this; raw data is proving that blogs are a superior tool for marketing online, with 55% of marketers saying that blogging is their top inbound marketing priority.
Running a blog is a straightforward concept. What you do is publish articles related to the topic of your website and do it regularly.
From a technical point of view, WordPress has blogging tools built right into it from the get-go. WordPress started as a blogging platform.
To create a new blog post, all you need to do is go to Posts → Add New (from your WordPress dashboard).
The process of creating a blog post works nearly the same as creating a new page. The editing panel looks nearly the same (the screenshot below), and the options are mostly the same as well.
One of the few differences is that you can also assign your posts to categories and tags.
Once you’re done working on a blog post, click on “Publish.”
To make your posts easily accessible, you should designate one of your pages to serve as the main blog listing for the posts.
- To do it, first, go to Pages → Add New and create a blank page. Call it “BLOG” – just to make things clear.
- Next, go to Settings → Reading, and select your newly created Blog page as the “Posts page”.
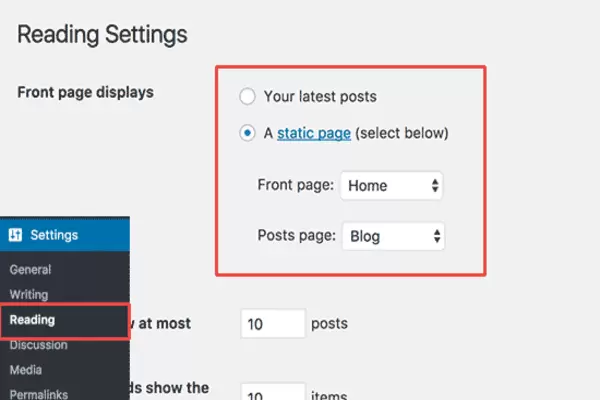
At this stage, you can navigate to that new page and see all your recent blog posts there. If you’re going to create a lot of content for your blog, consider an SSL certificate so that your readers feel safe while browsing through it.
Of course, the tough part about starting a blog is writing blog posts regularly and making them attractive for people to read.
Also Read: All You Need to Know about WordPress Theme 2023
Step 7: Adjust your site navigation
With all your key pages online (and perhaps your blog started as well), it’s now a good moment to adjust your site’s navigation menus and make it overall easier to consume for the visitors.
We’ll focus on two elements here:
(a) Menus
Menus are the primary vehicle through which visitors navigate your site, thus they’re crucial when figuring out how to make a website.
Depending on your theme, you will have a couple of options to choose from regarding menu settings. Here’s what you can usually do (on Hestia’s example):
First, go to Appearance → Menus in your WordPress dashboard.
To the left, there are all the pages you can choose to add to a menu. To the right, you can see the menu structure itself and all its settings.
Let’s start by selecting a couple of key pages and adding them to the menu. A good idea is to pick About, Contact, plus whatever other one or two pages you consider to be important, and add them to the menu.
The great thing about this whole panel is that you can drag and drop the menu items to reorder them.
When you’re done, select the menu location at the bottom. Usually, selecting the location labeled “Primary Menu” will result in showing the menu in the top section of the website. This is probably what you want for your main menu. Click on “Save Menu” to save the settings.
b) Widgets
Widgets are an old-school feature in WordPress. In simple terms, a widget is a small block of content that can be displayed in various places around the website.
The usual placement of those blocks is in the sidebar or the footer of the site.
To see what this might look like and to set your widgets, go to Appearance → Widgets in your WordPress dashboard.
Types of Website Hosting
After discussing in depth How to Make a WordPress Website, let us now discuss Website hosting.
Website hosting is an online service that allows you to publish your website or web application on the Internet. It involves storing and maintaining website files and applications on servers provided by a web hosting provider.
Web hosting providers lease space on their servers where you can upload the files that make up your website, including HTML files, CSS or JavaScript files, and multimedia content such as images and videos. Once these files are uploaded to a server, anyone with the correct website address or URL can access them online. through internet.
The Role of a Web Host
Web hosting providers can be compared to the real estate agents of the digital world. The primary role of web hosting is to provide the infrastructure that houses these servers. They manage sprawling data centers brimming with servers they lease to website owners.
Some additional responsibilities of web hosting providers include:
Server Maintenance and Support: Web hosts are in charge of ensuring the seamless operation of their servers. This encompasses hardware servicing, software upgrades, and troubleshooting potential technical problems.
Data Storage and Control: Web hosts house your website’s data on their servers and oversee the data transfer whenever a user visits your site.
Network Accessibility: Web hosts ensure that your website remains accessible to visitors 24/7 by maintaining a consistent high-speed internet connection to their servers.
Security Measures: Web hosts employ various security measures, such as firewalls, virus detection tools, spam filters, and more, to safeguard your website data against potential threats.
Resource Provision: Web hosts offer resources such as server space, bandwidth, and processing power. These resources are necessary for your website to function efficiently and serve visitors.
Customer Assistance: Most web hosts offer customer service to aid you in resolving any issues or answering any questions concerning your hosting service.
Traffic Management: Web hosts direct and manage traffic to your website. They ensure that when users enter your domain name in a web browser, they are directed to the correct server where your site is hosted.
Website Availability: A web host is responsible for making your website available online 24/7. They ensure that your site is consistently accessible to visitors.
In the following sections, we will delve further into web hosting and how it works. We will explore various hosting types, the data transfer process, the significance of domain names, and more. Gaining insight into these areas will enhance your understanding of “how web hosting operates,” helping you make knowledgeable decisions when selecting a web hosting service for your online projects.
Types of Web Hosting
There are several types of web hosting services available as follows:
- Shared Hosting: Multiple websites share the same server and its resources, making it an economical choice. However, performance may be affected by other sites on the server.
- Virtual Private Server (VPS) Hosting: A virtual server within a physical server. It offers more control and resources than shared hosting but is still cost-effective.
- Dedicated Hosting: You have an entire server for your website, ensuring high performance and control. This option is more expensive and suited for resource-intensive websites.
- Cloud-Based Hosting: Websites are hosted on a network of virtual servers. It provides scalability and reliability, as resources can be scaled up or down as needed.
- Managed WordPress Hosting: Specialized hosting for WordPress sites, with features like automatic updates and enhanced security.
- Colocation Hosting: You own the server, but it’s placed in a data center with professional management and infrastructure.
- Reseller Web Hosting: Allows individuals or businesses to resell hosting services with their branding.
Choosing a Web Hosting Provider
Once you’ve determined the hosting you need, the next step is to select a web hosting provider. The market is saturated with options, so making the right choice can feel overwhelming.
When selecting a web hosting provider, consider the following factors:
- Hosting Needs/ Website Type: Determine your specific requirements, such as the type of website you’re building (e.g., blog, e-commerce, or portfolio) and its expected traffic.
- Hosting Package: Choose an appropriate hosting package based on your needs, whether it’s shared hosting, VPS, dedicated server, or cloud hosting.
- Speed: Look for a hosting provider that offers fast loading times, as this is crucial for user experience and SEO.
- Security: Ensure the host provides robust security measures to protect your website from cyber threats and data breaches.
- Technical Support: Evaluate the quality of customer support and technical assistance. Responsive and knowledgeable support is essential when issues arise.
- Scalability: Choose a host that can accommodate your website’s growth. Scalability is vital as your site expands, ensuring it remains accessible and performs well.
- Cost/ Budget: Consider your budget, but remember that the cheapest option may not always provide the best service. Balance cost with the features and support you need.
- Traffic Volume: Your site’s traffic plays a significant role in your hosting choice. A website expecting high traffic will need more bandwidth and server resources to ensure a smooth user experience. Underestimating your traffic can lead to slow website speed or even downtime during traffic spikes.
- Server Location: The physical location of your host’s server can affect your site’s loading speed. Ideally, you want to choose a hosting provider with servers close to your audience’s location.
WordPress Website
FAQs
What is WordPress?
WordPress (also known as WP) is a web content management system (CMS) and web publishing platform that allows users to create and manage websites and blogs.
What do I need to build a WordPress website?
You’ll need the following three things to start your WordPress WordPress site:
- Domain name
- Website Hosting
Which is the best website builder platform?
There are many website builders available that will help you set up a website. We recommend using self-hosted WordPress as your website platform.
Is WordPress a free or paid platform?
WordPress is free, open source, and comes with thousands of pre-built website designs and extensions. It is extremely flexible and works with almost every third-party tool and service available to website owners.
What is a domain name?
A domain name is your website’s address on the internet. It serves as a human-readable label that allows users to navigate the internet easily. This is what your users will type in their browsers to reach your site (For example, wpwebtools.com or google.com).
What details are needed when you install WordPress?
When you install the WordPress, the following details are needed:
- URL ‒ your registered domain or address of your WordPress website.
- Language ‒ pick the primary language for WordPress.
- The Username ‒ the username you’ll use to log into the WordPress dashboard.
- The Administrator Password ‒ the password that you have to type in to enter the WordPress admin area.
- Email ‒ enter an active email address as it’ll be used for notifications and password reset.
- Website Title ‒ your website’s title
- Website Tagline ‒ a slogan or a short description of what your site is about.
What is Web hosting?
Website hosting is an online service that allows you to publish your website or web application on the Internet.
What are the types of web hosting?
Types of web hosting include:
- Shared Hosting: Multiple websites share the same server and its resources, making it an economical choice. However, performance may be affected by other sites on the server.
- Virtual Private Server (VPS) Hosting: A virtual server within a physical server. It offers more control and resources than shared hosting but is still cost-effective.
- Dedicated Hosting: You have an entire server for your website, ensuring high performance and control. This option is more expensive and suited for resource-intensive websites.
- Cloud-Based Hosting: Websites are hosted on a network of virtual servers. It provides scalability and reliability, as resources can be scaled up or down as needed.
- Managed WordPress Hosting: Specialized hosting for WordPress sites, with features like automatic updates and enhanced security.
- Colocation Hosting: You own the server, but it’s placed in a data center with professional management and infrastructure.
- Reseller Web Hosting: Allows individuals or businesses to resell hosting services with their branding.
What factors to consider when choosing web hosting?
- Hosting Needs/ Website Type: Determine your specific requirements, such as the type of website you’re building (e.g., blog, e-commerce, or portfolio) and its expected traffic.
- Hosting Package: Choose an appropriate hosting package based on your needs, whether it’s shared hosting, VPS, dedicated server, or cloud hosting.
- Speed: Look for a hosting provider that offers fast loading times, as this is crucial for user experience and SEO.
- Security: Ensure the host provides robust security measures to protect your website from cyber threats and data breaches.
- Technical Support: Evaluate the quality of customer support and technical assistance. Responsive and knowledgeable support is essential when issues arise.
- Scalability: Choose a host that can accommodate your website’s growth. Scalability is vital as your site expands, ensuring it remains accessible and performs well.
- Cost/ Budget: Consider your budget, but remember that the cheapest option may not always provide the best service. Balance cost with the features and support you need.
- Traffic Volume: Your site’s traffic plays a significant role in your hosting choice. Underestimating your traffic can lead to slow website speed or even downtime during traffic spikes.
- Server Location: The physical location of your host’s server can affect your site’s loading speed. Ideally, you want to choose a hosting provider with servers close to your audience’s location.
What are the roles of the web hosting?
Server Maintenance and Support: Web hosts are in charge of ensuring the seamless operation of their servers.
Data Storage and Control: Web hosts house your website’s data on their servers and oversee the data transfer whenever a user visits your site.
Network Accessibility: Web hosts ensure that your website remains accessible to visitors 24/7 by maintaining a consistent high-speed internet connection to their servers.
Security Measures: Web hosts employ various security measures, such as firewalls, virus detection tools, spam filters, and more, to safeguard your website data against potential threats.
Resource Provision: Web hosts offer resources such as server space, bandwidth, and processing power. These resources are necessary for your website to function efficiently and serve visitors.
Customer Assistance: Most web hosts offer customer service to aid you in resolving any issues or answering any questions concerning your hosting service.
Traffic Management: Web hosts direct and manage traffic to your website. They ensure that when users enter your domain name in a web browser, they are directed to the correct server where your site is hosted.
Website Availability: A web host is responsible for making your website available online 24/7. They ensure that your site is consistently accessible to visitors.
Best Guides for WordPress Website
- A WordPress Plugin: The Complete Guides 2023
- What is WordPress? A Complete guides 2023
- All You Need to Know about WordPress Theme 2023
- LiteSpeed Cache: The Best Settings for WordPress Websites
- Most Popular Brands That Are Using WordPress
- Important Pages That All WordPress Blogs Should Consider
If you liked this article, then please follow us on Facebook.
Popular on WPWebTools Right Now!
*This post contains affiliate links, which means that if you click on one of the product links and then purchase the product, we’ll receive a small commission. No worries though, you’ll still pay the standard amount so there’s no additional cost on your part.

